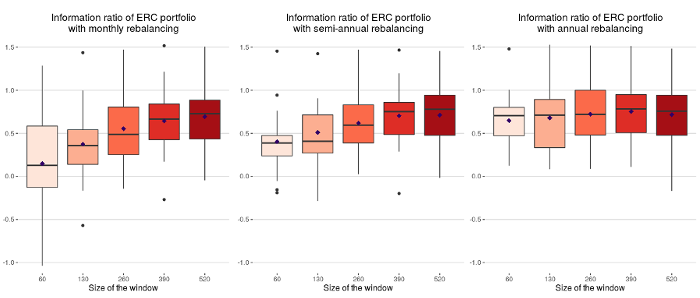
Equal risk contribution (ERC) and inverse-volatility portfolios that are frequently rebalanced should be rebalanced using large window sizes of recent data in order to generate the best information ratios.
Le ratio d'information mesure les rendements excédentaires par unité de risque de volatilité, évaluant essentiellement la régularité de la surperformance d'une stratégie par rapport à un indice de référence. Plus le ratio d'information est élevé, mieux c'est.
A report by Quantilia found that large window sizes, in this case 390 and 520 days, seem to deliver the best mean rolling information ratios for portfolios that are rebalanced monthly, quarterly or semi-annually.
Window size refers to the number of days’ worth of data used when calculating adjusted portfolio weights.
In the case of annual rebalancing, the window size used for rebalancing does not have a material effect on information ratios, and so no recommendation is given in the report. On the other hand, more frequent portfolio rebalancing requires larger window sizes of data in order to maintain high information ratios.
The Quantilia report was based on 20 baskets of 20 strategies each, with a split between alpha and beta strategies and exposure to different asset classes and strategy providers. The different window sizes used were 60, 130, 260, 390 and 520 business days, while the weighting schemes used were ERC and inverse-volatility.
Les fonds ERC sont pondérés de telle sorte que chaque titre contribue de manière égale au risque total du portefeuille, réduisant ainsi la concentration du risque du portefeuille. Cette approche est similaire à celle de l'inverse de la volatilité, bien que la stratégie ERC tienne également compte des corrélations entre les titres au sein du portefeuille.
Smart beta strategies in particular require relatively frequent portfolio rebalancing in order to keep them within their predefined strategy boundaries. Some strategies, or underlying risk factors, require more frequent rebalancing than others.


